54 basic surgical instruments pdf
The 54 basic surgical instruments are essential tools in modern surgery, designed for tasks like cutting, dissecting, suturing, and retracting. They are categorized by function and material, with German-grade stainless steel being common due to its durability and corrosion resistance. These instruments are fundamental for medical professionals, ensuring efficiency and precision during procedures. Understanding their proper use and care is crucial for successful surgical outcomes and longevity of the tools.
Overview of the Importance of Surgical Instruments in Modern Surgery
Surgical instruments are critical in modern surgery, enabling precise and efficient procedures. They reduce fatigue, enhance dexterity, and minimize operative time. Proper tool selection ensures optimal outcomes, while high-quality materials like German-grade stainless steel provide durability and corrosion resistance. Mastery of these instruments is vital for surgeons, promoting consistency and safety in demanding surgical environments.
Efficiency and Fatigue Reduction in Surgical Procedures
Modern surgical instruments are designed to enhance efficiency and reduce user fatigue during lengthy procedures. Ergonomic handles and balanced weights minimize strain, allowing for precise control. Proper tool selection and strategic placement on the Mayo table streamline workflows, ensuring smooth execution of tasks. This focus on efficiency contributes to better surgical outcomes and reduced operator discomfort.
Materials and Manufacturing of Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments are crafted from high-quality materials like German-grade stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance and durability. Precision engineering ensures reliability and consistent performance.
German-Grade Stainless Steel in Surgical Tools
German-grade stainless steel is prized for its corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for surgical instruments. It withstands repeated sterilization and maintains sharpness, ensuring reliability and longevity. This high-quality material is crafted with precision, minimizing wear and tear, and is a cornerstone in manufacturing durable surgical tools for consistent performance.
Corrosion Resistance and Sterilization Capabilities
Surgical instruments made from German-grade stainless steel excel in corrosion resistance and withstand rigorous sterilization processes. Their durability ensures they remain functional after repeated cleaning and disinfection. This material’s ability to endure high temperatures and harsh chemicals makes it ideal for maintaining hygiene and longevity, ensuring reliable performance in demanding surgical environments.
Categorization of Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments are categorized into groups such as cutting/dissecting, suturing, clamping, grasping, holding, and retracting. Each category serves specific functions, ensuring efficiency and precision during procedures.
Cutting and Dissecting Instruments
Cutting and dissecting instruments are essential for making precise incisions and separating tissues. They include scalpels, knives, and scissors. Scalpels feature interchangeable blades, while dissecting scissors are used for fine tissue separation. Proper technique is vital to avoid damage, ensuring smooth surgical progression.
Suturing and Clamping Instruments
Suturing instruments, such as needle holders, are used to grasp and maneuver sutures, while clamps secure tissues or blood vessels. These tools are crucial for maintaining control during procedures, ensuring precise suturing and effective hemostasis. Proper handling and selection are essential for optimal surgical outcomes.
Grasping, Holding, and Retracting Instruments
Grasping, holding, and retracting instruments are vital for exposing surgical sites and maintaining tissue control. Forceps and retractors are commonly used to grip tissues or structures gently, while retractors help pull back surrounding tissues for better visibility. These tools enhance accessibility during procedures, ensuring precise manipulation and minimizing damage to delicate areas, making them indispensable in modern surgical practices.
Key Features of Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments feature ergonomic handles, durable materials, and precise locking mechanisms, ensuring control and longevity. These designs enhance surgical precision and reduce operator fatigue significantly.
Handle Design and Finger Rings
Ergonomic handles with contoured finger rings enhance grip comfort and control, reducing fatigue during prolonged procedures. The design ensures precise alignment and balance, optimizing surgical accuracy and ease of use.
Shanks and Jaws of Surgical Instruments
The shank connects the handle to the working jaws, ensuring precise alignment and durability. Jaws vary in design, with straight or curved configurations, enabling specific functions like cutting, clamping, or dissecting. Their alignment and tension are critical for effective performance, ensuring secure grip and smooth operation during surgical procedures.
Ratchets and Locking Mechanisms
Ratchets and locking mechanisms ensure secure grip and stability during surgical procedures. These components prevent slippage, maintaining precise control over tissues or materials. Their durability and smooth operation are vital for reliable performance, minimizing fatigue and enhancing surgical accuracy. Proper alignment and tension in these mechanisms are essential for optimal functionality.
Common Surgical Instruments in the List
The list includes scalpels, forceps, retractors, and suction tips, essential for cutting, grasping, and suctioning. These tools are vital for precise surgical tasks and patient safety.
Scalpel Blades and Handles
Scalpel blades and handles are fundamental in surgery for making precise incisions. Blades vary by type, such as 10, 11, and 15, each suited for specific tasks. Handles are designed for ergonomic grip, reducing fatigue. Proper attachment of blades to handles is crucial for safety and effectiveness, ensuring secure locking mechanisms to prevent accidental detachment during use.
Tissue Scissors and Forceps
Tissue scissors and forceps are essential for precise tissue handling. Tissue scissors, such as Mayo and Metzenbaum, are designed for cutting soft tissues with sharp, curved blades. Forceps, including Alligator and Adson, are used for grasping and holding tissues firmly. Made from durable materials like stainless steel, they ensure effective manipulation and control during surgical procedures.
Needle Holders and Suction Tips
Needle holders, like the Hegar and Mathieu, securely grip needles, enabling precise suturing. Suction tips, such as the Poole and Frazier, are used to remove fluids, improving visibility. Both instruments are crafted from high-quality materials for durability and sterilization, ensuring optimal performance in various surgical tasks.
Usage in Surgical Procedures
Surgical instruments are strategically placed on the Mayo table based on frequency of use, ensuring efficiency. Their arrangement optimizes accessibility, minimizing delays and enhancing surgical precision and visibility.
Frequency of Use and Strategic Placement
In surgical settings, instruments are arranged based on their frequency of use to enhance efficiency. High-use tools are placed within easy reach, while less common ones are positioned farther away. This strategic organization on the Mayo table ensures seamless accessibility, reducing delays and improving surgical workflow. Proper placement is crucial for maintaining focus and precision during procedures.
Instrument Setup on the Mayo Table
The Mayo table is central to surgical organization, holding essential instruments within the surgeon’s immediate reach. Instruments are grouped by function, with cutting tools like scalpels and scissors placed near the primary work area. Retractors and forceps are positioned to facilitate easy access, ensuring a streamlined workflow. This setup minimizes distractions and allows the surgical team to focus on the procedure efficiently.
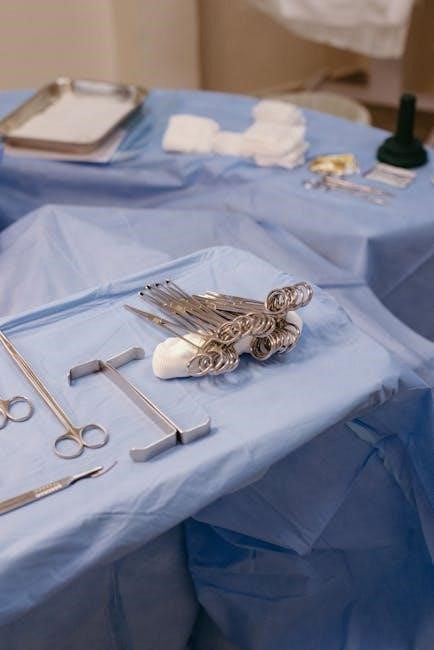
Safety and Techniques in Using Surgical Instruments
Proper handling of surgical instruments is crucial to prevent damage to surrounding tissues and ensure patient safety. Skilled techniques minimize risks and enhance procedural efficiency.
Preventing Damage to Surrounding Structures
Precise handling and correct technique are vital to avoid damaging surrounding tissues during surgery. Using appropriate tools ensures minimal impact on nearby structures. Durable materials like German-grade stainless steel enhance instrument longevity, reducing the risk of breakage. Proper alignment and controlled movements are essential for safe and effective procedures, ultimately ensuring patient safety and optimal surgical outcomes.
Proper Handling and Skill Requirements
Proficiency in handling surgical instruments is crucial for surgeons and medical staff. Proper grip, alignment, and technique prevent fatigue and ensure precision. Training and practice are essential to master the use of tools like scalpels, forceps, and retractors. Skillful handling minimizes risks, enhancing patient safety and procedural success, while also extending instrument longevity through correct usage and care.
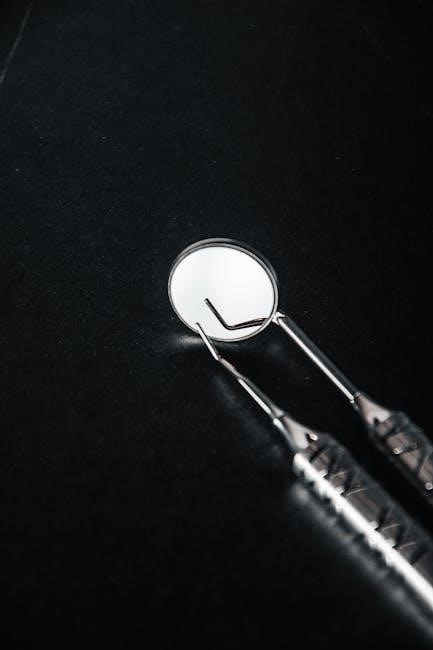

Maintenance and Longevity of Surgical Tools
Regular cleaning, sterilization, and proper storage are vital for extending the life of surgical instruments. High-quality materials, like German-grade stainless steel, enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring longevity.
Cleaning and Sterilization Processes
Proper cleaning and sterilization are crucial for maintaining surgical instrument longevity. Instruments are cleaned using ultrasonic devices or enzymatic solutions to remove debris, then sterilized via autoclaving. This ensures they remain free from contamination and functional for repeated use, adhering to infection control standards and patient safety protocols.
Storage and Handling Practices
Surgical instruments should be stored in dry, protective cases to prevent damage and corrosion. Proper handling involves using padded trays and avoiding stacking to maintain instrument integrity. Regular inspection ensures tools remain functional, while organized storage systems facilitate quick access during procedures, enhancing efficiency and safety in the operating room environment.
FAQs and Common Queries
FAQs about the 54 basic surgical instruments address material quality, maintenance, and usage; Queries often include ideal storage methods and troubleshooting common instrument malfunctions, ensuring optimal performance.
Material-Related Questions
FAQs often inquire about the durability and composition of surgical tools. German-grade stainless steel is commonly used, offering corrosion resistance and ease of sterilization. This material ensures longevity and withstands repeated cleaning processes, making it ideal for surgical environments. Its non-reactive properties minimize the risk of contamination, ensuring patient safety and optimal tool performance during procedures.
Flashcards for Learning Instruments
Flashcards are a popular tool for memorizing the 54 basic surgical instruments. They typically feature high-quality images and names of instruments, along with their uses. This method aids in quick recall during exams or surgical prep. Many resources offer digital flashcards, allowing users to test their knowledge and track progress. Categorized lists and interactive tools enhance learning efficiency for medical students and professionals.
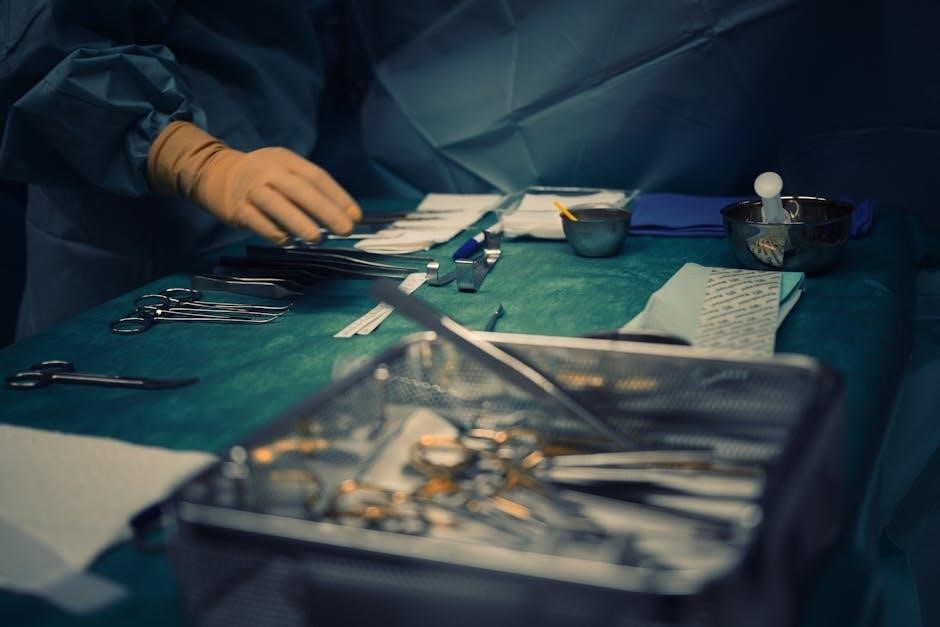
Learning Resources for Surgical Instruments
Flashcard tools, categorized lists, and PDF guides provide organized study materials for mastering the 54 basic surgical instruments, aiding in efficient learning and quick reference.
Flashcard Tools for Memorization
Flashcard tools are effective for memorizing the 54 basic surgical instruments, offering interactive learning and quick recall. Platforms like CSTSetup’s PRO flashcard tool organize instruments by category, allowing users to test their knowledge and enhance retention. These tools are invaluable for medical students and professionals, providing a structured approach to mastering surgical instrumentation efficiently.
PDF Guides and Categorized Lists
PDF guides and categorized lists provide comprehensive overviews of the 54 basic surgical instruments, organizing them by function and usage. These resources detail instruments like cutting/dissecting scissors, needle holders, and forceps, aiding in understanding their roles and setup on the Mayo table. They are invaluable for training and quick reference, ensuring efficient instrument identification and strategic placement during procedures.
Advanced Surgical Instrumentation
Advanced surgical instrumentation includes robotic systems and interchangeable tools, enhancing precision and versatility in modern procedures. These innovations allow for minimally invasive techniques and improved surgical outcomes.
Robotic Surgical Systems
Robotic surgical systems are electronically powered tools with multiple arms and interchangeable surgical instruments. These systems enable precise minimally invasive procedures, operated via a console by surgeons. They enhance dexterity, reduce human error, and improve outcomes. Surgical technicians assist by replacing instruments during procedures, making robotic systems integral to modern advanced surgery, offering unmatched accuracy and efficiency in complex operations.
Interchangeable Tools in Modern Surgery
Interchangeable tools in modern surgery offer versatility and precision, allowing surgeons to adapt to diverse procedures seamlessly. These modular instruments enable quick swaps during operations, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Designed for compatibility with robotic systems, they improve dexterity and minimize tissue trauma, making them indispensable in complex surgeries and advancing surgical outcomes significantly.
Mastery of the 54 basic surgical instruments is vital for surgical success. Continuous learning and advancements in technology will shape the future of surgical instrumentation, ensuring better patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Importance of Mastery in Surgical Instrumentation
Mastery of surgical instrumentation is a cornerstone for surgeons and surgical technicians, ensuring precision, efficiency, and patient safety. Proficiency in handling tools reduces fatigue and complications, enabling better outcomes. Understanding each instrument’s purpose and proper technique is critical for minimizing errors and enhancing surgical success. This skill fosters confidence and competence, adhering to surgical standards and minimizing complications.
Resources for Further Study
For deeper understanding, resources like flashcards, categorized lists, and detailed PDF guides are available. Platforms such as CSTSetup offer comprehensive tools, including flashcard sets and categorized lists of instruments. These resources aid in memorization, setup guidance, and strategic placement of tools during procedures, ensuring mastery and effective utilization in surgical environments.